
Inflammation
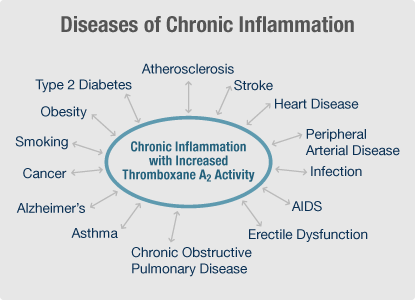
Inflammation is one of the common denominators of disease as well as brain dysfunction. Every chronic disease is inflammatory in nature. Learning how to prevent and reverse inflammation will go a long way toward preventing disease, as well as slowing the aging process.
What causes inflammation? Most importantly, the standard American diet causes inflammation. How does our diet cause inflammation? One way is excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates. Sugar and white flour have an inflammatory effect on the body. Acidity is another problem. Most Americans eat an acidic diet caused by too much salt, sugar, white flour, dairy, meat and cola drinks. Many experts consider over-acidity to be one of the major causes of chronic inflammation, with increasing acidity causing increasing amounts of inflammation.
Lifestyle modifications such as eating a healthier diet, getting enough sleep and exercising all help with decreasing inflammation.
Supplements to aid with reducing inflammation
Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)- Amino acids (leucine, isoleucine and valine are unique from other amino acids because they can be burned as fuel within muscle tissue, rather than in the liver, allowing for increased muscular endurance and faster recovery . Leucine plays an important role in muscle protein synthesis, while, isoleucine and valine seem more effective at producing energy and regulating your blood sugar levels.
BCAAs also help your muscles feel less sore after exercise. In one study participants who were given BCAA supplements rated their muscle soreness levels as much as 33% lower than those given a placebo. In some cases, those given BCAAs also performed up to 20% better when they repeated the same strength-training tests 24–48 hours later
BCAAs allow people on low calorie diets or when intermittent fasting to burn fat and not muscle and they aid with decreasing appetite.
Best Dosages of BCAAs
BCAAs are important to have on a daily basis, many protein sources, such as meat and eggs, already provide BCAAs. Supplementation is unnecessary for people with a sufficiently high protein intake (1-1.5g per kg of bodyweight a day or more).
For intense exercise and training, 4-8 grams before a workout and 4-8 grams after is optimal. Smaller dosages are still effective, but the higher doses are linked to increased performance and recovery. Also, for cardio or aerobic exercise, BCAA’s immediately before or during the workout will increase performance.
Curcumin / Turmeric – Turmeric is a spice derived from the rhizome and root of the Curcuma longa plant which I native to Asia. This orange herb has been traditionally used for centuries by Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine.
Curcumin is the most powerful active anti-inflammatory compound within turmeric and has been shown to be a powerful suppressor of chronic inflammation. With a high enough dosage curcumin has the ability to pull the body out of a strong inflammatory response at the cellular level. Due to curcumin’s ability to reduce inflammation, the University of Maryland Medical Center states that supplementing with curcumin may help to relieve symptoms of osteoarthritis, or pain and stiffness in the joints.
Blood sugar imbalances and insulin resistance are huge factors that promote inflammatory conditions in the body. Curcumin can decrease blood sugar as it improves insulin function by improving its binding capacity to sugar. Curcumin also reduces the activity of liver enzymes that release sugar into the bloodstream while activating enzymes that store sugar as glycogen.
Curcumin stimulates the gallbladder to produce bile, and consuming turmeric on a regular bases may help to improve digestion, reduce bloating as well as treat other digestive disorders
Research done by the Life Extension Foundation found that the active ingredients in curcumin target ten factors involved in cancer development. Curcumin supplementation was shown to destroy cancer cell by disrupting the cancer cell cycle and stop further cancer cell formation.
Best dosages of curcumin
For optimal curcumin absorption, it is necessary to combine turmeric with good fats such as coconut oil, milk or olive oil. You will also want to add a dash of black pepper to enhance curcumin uptake. An official dosage has not yet been established by scientific literature. However, studies involving human patients with cancer found that curcumin doses of 3.6 grams or more daily had the best effect., other research recommend, 2-8 grams of curcumin daily for inflammatory disorders.
Fish oil/Omega 3–Higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids are linked to lower body fat, protecting the brain and making your better at problem solving.
Two studies published in the Nutritional Neuroscience and Aging and Disease journal state that by reducing inflammation, and reducing blood pressure Omega 3 fatty acids support a critical role in maintaining specific brain structures related to intelligence, memory and healthy aging of the brain.
Best dosages of fish oil/omega 3
For general brain health: 2-4 grams of pharmaceutical grade fish oil/day (GNC or Nordic are comparable brands)
Green Tea- Rich in polyphenol flavonoids, a potent anti-oxidant, green tea consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart disease and stroke. Research published by Harvard demonstrates that people who drink at least one cup of tea daily have a 44 percent lower risk of heart attack. Some animal studies have demonstrated that green tea also lowers cholesterol levels.
Along with the natural fluoride found in tea, polyphenols and catechins are associated with killing bacteria that cause tooth decay, bad breath, and gum disease-the number one cause for tooth loss.
In one study, participants who drank four cups of tea daily burned an average of 67 additional calories a day. Drinking at least three cups a day is recommended to raise the body’s metabolic rate. For optimal antioxidant benefits consuming 3-4 cups/day is recommended
Magnesium- Magnesium is a vital nutrient that is often deficient in modern diets. The current RDA for adults is between 320 and 420mg daily, and the average US intake is around 250mg daily.
A 2006 study found that Magnesium was usually effective for treatment of depression in general use. Related and accompanying mental illnesses in these case histories included traumatic brain injury, headache, suicidal ideation, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, postpartum depression, cocaine, alcohol and tobacco abuse, short-term memory loss and IQ were also benefited.
Dietary deficiencies of magnesium, coupled with excess calcium and stress may cause many cases of other related symptoms including agitation, anxiety, irritability, confusion, asthenia, sleeplessness, headache, delirium, hallucinations and hyperexcitability.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16542786/
Melatonin- Melatonin is a hormone made by the pineal gland, a small gland in the brain. Melatonin helps control your sleep and wake cycles. Very small amounts of it are found in foods such as meats, grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Studies report that melatonin may help improve the amount of time it takes to fall asleep, as well as increasing sleepiness and sleep duration. According to human research, melatonin may benefit children with insomnia. Melatonin has been studied for sleep-wake disorders in children and adolescents.
Several human trials suggest that melatonin taken by mouth, started on the day of travel (close to the target bedtime at the destination) and continued for several days may help with jet lag. It reduces the number of days needed to begin a normal sleep pattern, shortens the time it takes to fall asleep, improves alertness, and reduces daytime fatigue.
Some people will only require 0.1 to 0.3 mg of Melatonin to sleep better. If using 3 mg per night is not effective after 3 days, try increasing your dosage to 5 – 6 mg 1 hour before going to bed. The correct dose should give you a restful sleep without daytime irritability or drowsiness.
Probiotics- The human gut contains 10 x more bacteria that all the human cells in the entire body recent evidence suggests that our gut microbiome affects various elements of brain function and heart health , including mood, cognition, stress resilience, atherosclerosis and hypertension.
Your intestinal bacteria are part of your immune system, and researchers are discovering that microbes play instrumental roles in countless areas of your health, including your weight . Researchers have discovered a difference in gut bacteria between the overweight and those of normal weight. Changes in the gut flora can increase the rate at which we absorb fat and carbohydrates and change the proportion of signaling molecules in the gut and the brain. There’s a feedback loop between the foods you crave and the composition of the bacteria in your gut that depend on those nutrients for their survival. In other words, the bacteria is your gut are responsible for your food cravings. If you change your bad bugs for good bugs you can resolve unhealthy food cravings.
It’s common for people who suffer from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) to also struggle with depression. A small study published in the journal Gastroenterology suggests that taking a probiotic supplement may provide relief from both conditions. Scientists from McMaster University in Canada recruited 44 adults with IBS as well as mild to moderate anxiety or depression. They were followed for 10 weeks; half took a daily dose of the probiotic Bifidobacterium longum, and half took a placebo. After six weeks, twice as many people who took the probiotic had decreased depression scores compared to those who took the placebo: 64% versus 32%. When people in the study were given functional MRI scans, the researchers found that improved depression scores were associated with changes in activity of several brain areas involved in mood regulation
In findings published in the journal Nutrients, Canadian researchers from McMaster University describe how gut bacteria can disrupt heart health in that it leads to clogged arteries/high cholesterol and high blood pressure. Probiotics help reduce blood cholesterol in three different ways: Probiotics create acids that counter cholesterol production; Probiotics break down liver bile acid, Probiotics actually eat cholesterol, they have been shown to break down cholesterol and use it for nourishment.
Guidelines for Probiotic Supplementation
Include healthy sources of probiotics in your diet fermented foods such as Kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt all have active probiotic cultures. If supplementing with probiotics, supplement with 50-100 billion CFU containing at least three different strains Bifidobacterium spp. Lactobacillus spp. Streptococcus spp. Total Daily Dose: 50-100 billion CFUs/day